Cells Unit Review Part 1 Organic Molecule Review
Which jail cell type contains membrane-leap organelles?
- Prokaryotic
- Eukaryotic
- Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic
Cells that contains streaming cytoplasm
- are prokaryotic
- are eukaryotic
- can be either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cells that practice not take histone proteins associated with their DNA
- are prokaryotic
- are eukaryotic
- tin can be either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cells that have DNA as their genetic material include
- simply prokaryotic cells
- but eukaryotic cells
- both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Animals, plants, fungi, and protists have cells that are
- exclusively prokaryotic
- exclusively eukaryotic
- both prokaryotic and eukaryotic
- neither prokaryotic and eukaryotic
Leaner have cells that are
- exclusively prokaryotic
- exclusively eukaryotic
- both prokaryotic and eukaryotic
- neither prokaryotic nor eukaryotic
Viruses differ from cells in which of the following ways?
Cells that comprise a nucleus
Prokaryotic cells comprise
Eukaryotic cells contain
Differences between a plant and animate being cell include:
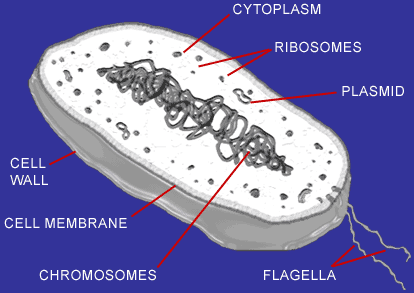
The cell pictured above is characteristic of
The master office of the Golgi apparatus is the:
- synthesis of Dna
- processing of large molecules such as proteins and lipids
- generation of cellular energy in the form of ATP
- storage of water
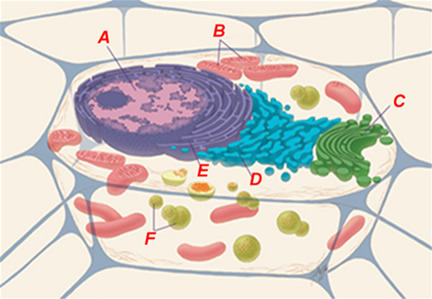
Though some Dna is plant in the mitochondria, almost of the genetic data of the prison cell is stored
- in the construction labeled "A"
- in the construction labeled "B"
- in the construction labeled "C"
- in the construction labeled "D"
- in the structure labeled "E"
- in the structure labeled "F"

Generation of energy through cellular respiration takes place
- in the structure labeled "A"
- in the structure labeled "B"
- in the construction labeled "C"
- in the structure labeled "D"
- in the structure labeled "Eastward"
- in the construction labeled "F"

Ship of lipids takes place
- in the structure labeled "A"
- in the construction labeled "B"
- in the structure labeled "C"
- in the construction labeled "D"
- in the construction labeled "E"
- in the structure labeled "F"

Ribosomes attach to
- the construction labeled "A" giving it a "rough" advent
- the structure labeled "B" giving it a "rough" advent
- the structure labeled "C" giving it a "rough" appearance
- the construction labeled "D" giving information technology a "rough" advent
- the construction labeled "E" giving information technology a "crude" appearance
- the construction labeled "F" giving it a "rough" appearance

Which of the following helps you determine that the jail cell in a higher place is NOT a plant cell?
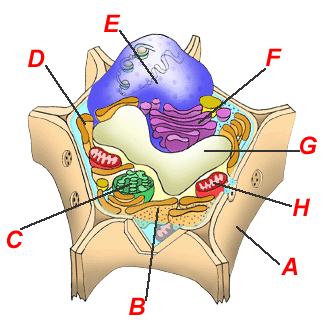
Which of the following would help you conclude that the prison cell shown here is a institute cell?

The structure labeled "A" has the role of
- providing rigidity and preventing water loss
- converting sunlight to chemical energy
- processing and transporting macromolecules such every bit proteins and lipids
- protecting the cell'southward Deoxyribonucleic acid

The structure labeled "B" has the function of
- providing rigidity and preventing water loss
- converting sunlight to chemical energy
- transporting proteins produced by the fastened ribosomes
- transporting fats to the nucleus

The structure labeled "C" has the function of
- providing rigidity and preventing water loss
- converting sunlight to energy
- transporting proteins produced by the attached ribosomes
- transporting fats to the nucleus

The structure labeled "G" has the function of
- storage and support
- converting sunlight to energy
- transporting proteins produced by the attached ribosomes
- converting nutrient energy to ATP

The structure labeled "H" has the role of
- storage and support
- converting sunlight to free energy
- transporting proteins produced by the attached ribosomes
- converting food energy to ATP

Processing of large molecules such as proteins and fats takes identify
- in the structure labeled "H"
- in the structure labeled "B"
- in the construction labeled "C"
- in the structure labeled "F"
- in the structure labeled "Yard"

Tour de France winner Greg Lemond retired from competitive cycling when he was diagnosed with a disorder that prevented his cells from producing sufficient free energy for vigorous activity. Which organelle was the source of his malady?
- The construction labeled "A"
- The construction labeled "B"
- The structure labeled "C"
- The structure labeled "D"
- The construction labeled "Eastward"
The antibiotic tetracycline interferes with the function of bacterial ribosomes. Because bacterial ribosomes are dissimilar from the ribosomes in human cells, taking tetracyline merely stops
- the product of bacterial protein
- the formation of the bacterial cell wall
- the storage of h2o in bacterial cells
- the processing and send of lipids in the bacterial cell
The procedure past which cells expel, or secrete, large molecules is known as
- pinocytosis
- phagocytosis
- exocytosis
- endocytosis
Which respond correctly describes the lipid bilayer?
- lipids are hydrophobic; phosphates are hydrophilic
- lipids are hydrophilic; phosphates are hydrophobic
- lipids are hydrophilic; phosphates are hydrophilic
- lipids are hydrophobic; phosphates are hydrophobic
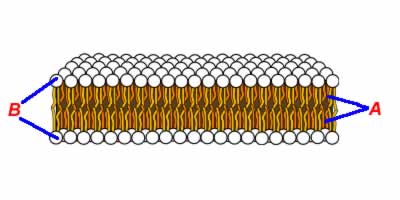
In the image depicted higher up, the office of the bilayer that is hydrophobic includes
- region A merely
- region B only
- both region A and region B
- neither region A nor region B

In the paradigm depicted in a higher place, the function of the bilayer labeled "A"
- are the charged phospates
- are the hydrophobic lipids
- are the transport proteins
- are the glycoproteins

In the image depicted in a higher place, the part of the bilayer labeled "B"
- are the charged phospates
- are the hydrophobic lipids
- are the transport proteins
- are the glycoproteins
2 types are endocytosis are called
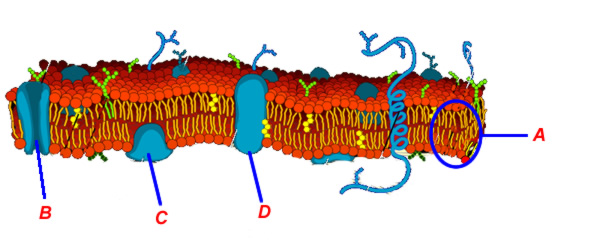
In the image above, the transport protein
- is labeled "A"
- is labeled "B"
- is labeled "C"
- is labeled "D"

In the paradigm in a higher place, the phospholipid bilayer
- is labeled "A"
- is labeled "B"
- is labeled "C"
- is labeled "D"

In the image above, the structures labeled "B", "C" and "D" are all
- institute only in fauna cells
- proteins
- phospholipids
- found but in establish cells

The construction whose function is to allow substances to lengthened from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
- is labeled "A"
- is labeled "B"
- is labeled "C"
- is labeled "D"
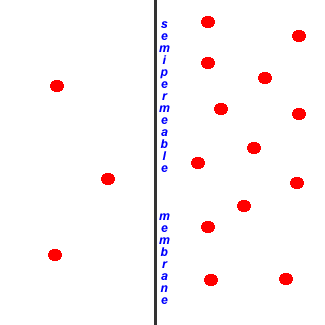
Move of the modest molecules from left to right beyond the membrane

Motion of the minor molecules from right to left across the membrane

If the small molecules are water molecules, then the move from right to left across the membrane
- is called pinocytosis
- is chosen osmosis
- is called active transport
- volition not occur in a healthy cell
When salt is poured on a slug, it dies considering
- water moves out of the slug, causing dehydration
- salt moves into the slug, poisoning it
- water moves into the slug, causing it to cracking
- common salt moves out of the slug, depriving it of essential minerals
In passive diffusion, substances always move
- from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
- from an surface area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration
- from an expanse with more of the molecules to an expanse with fewer of the molecules
- from an area with fewer of the molecules to an expanse with more of the molecules
Which of these elements MUST be present in society for a molecule to be considered organic?
Which six elements make upwardly almost of the mass of living cells?
The bonds between atoms in organic molecules such equally sugars, fats and proteins are
- ionic bonds
- covalent bonds
- metallic bonds
- nuclear bonds
Proteins are made up of long bondage of which of these building blocks?
- sugars
- amino acids
- fat acids
- glycerol molecules
- nucleic acids
The organic molecules that carry the genetic lawmaking of a prison cell belong to which course of molecules
- nucleic acids
- proteins
- lipids
- starches
- steroids
Which of the post-obit would provide the greatest amount of energy when burned by cells?
- one gram of poly peptide
- ane gram of fat
- ane gram of sugar
- 1 gram of starch
The edifice blocks of a triglyceride molecule are
- amino acids and glycerol
- nucleic acids and amino acids
- glycogen and fatty acids
- fatty acids and glycerol
- sugars and starches
Which of the following is not normally a function of proteins in healthy cells?
- a component of cell membranes
- long-term free energy storage
- functioning as enzymes
When sugars polymerize in long chains, they may form any of the following except:
- glycogen
- cellulose
- starch
- proteins
Examples of nucleic acids include
- Deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA
- amino acids and fatty acids
- sugars and starches
- fats and proteins
Which of the following is an example of an organic chemic compound?
- sodium chloride, NaCl
- glucose, Chalf dozenH12O6
- carbon dioxide, COii
- sufur trioxide, SO3
When electrons are shared between atoms of nonmetals, a(due north) ________________ bond is formed.
- covalent
- ionic
- metallic
- nuclear
When a bail results from the transfer of electrons between atoms, information technology's a(n) ________________ bond that has formed.
- covalent
- ionic
- metal
- nuclear
Assuming y'all can digest all of them, which of the post-obit carbohydrates has the greatest energy value per gram?
- carbohydrate
- starch
- cellulose
- glycogen
- none of these, because they all have the aforementioned energy value
Source: https://www.sciencegeek.net/Biology/review/U1Review.htm
0 Response to "Cells Unit Review Part 1 Organic Molecule Review"
Publicar un comentario